by Tony Lee.
I have had a few internal network penetration tests now in which I came across the following finding identified by McAfee Vulnerability Manager (MVM): "Firebird SQL Default Credentials Detected". So I figured I'd share with you what is required to interact with the database and provide you with ideas on what you can do after you connect. Tune in for a future article on more fun with Firebird.
In 2000, Borland decided to release InterBase 6.0 as Open Source. Firebird is an independent development, beginning with these sources, driven by an Open Source Community and funded by the Firebird Foundation.”
--Source: http://www.destructor.de/firebird/index.htm
--Source: http://www.flamerobin.org/
It is easily installed on BackTrack (or other distros that utilize apt):
<
To run, launch X windows and type:
You may get the following error message, ignore it and continue:
Next, right click on the server that you just registered, choose "Retrieve server version" and provide your credentials. The default firebird username and password is usually:
Username: SYSDBA
Password: masterkey
You should be provided the version number as shown below:
To add a user, just click "Add User" and provide the required information! To modify other users (including changing their passwords) by clicking on the “details” icon which looks like a magnifying glass over a piece of paper.
Common command line options:
To add a "
To modify users, define the username and password used to connect to the database with "
Notice that you specify “sysdba” twice in the command:
With the
I have had a few internal network penetration tests now in which I came across the following finding identified by McAfee Vulnerability Manager (MVM): "Firebird SQL Default Credentials Detected". So I figured I'd share with you what is required to interact with the database and provide you with ideas on what you can do after you connect. Tune in for a future article on more fun with Firebird.
What is the Firebird Database?
“Firebird is a relational SQL database offering many ANSI SQL-92 features that runs on Linux, Windows, and a variety of Unix platforms. Firebird offers excellent concurrency, high performance, and powerful language support for stored procedures and triggers. It has been used in production systems, under a variety of names (the most famous being "InterBase") since 1981.In 2000, Borland decided to release InterBase 6.0 as Open Source. Firebird is an independent development, beginning with these sources, driven by an Open Source Community and funded by the Firebird Foundation.”
--Source: http://www.destructor.de/firebird/index.htm
Identifying Firebird Databases
Vulnerability scanners
Perhaps the easiest method to find Firebird databases is by using a vulnerability scanner. MVM and Nessus will also let you know if the database is configured with default credentials. Here are the findings from MVM and Nessus:- McAfee Vulnerability Manager (MVM): Firebird SQL Default Credentials Detected
- Nessus: Firebird Default Credentials
Port scan
You can use any port scanner to check for TCP port 3050. Note that this is just the default port and can always be changed by the admin. A simple port scan to find it would be: root@bt:~# nmap -sS -T4 -PN -p 3050 192.168.1.0/24
Firebird Database Tools
There are plenty of tools to interact with Firebird. Most commonly that can be grouped into either a client or a Database management tool. We'll look at one of each.FlameRobin (Client)
"FlameRobin is a database administration tool for Firebird RDBMS. Their goal is to build a tool that is:- lightweight (small footprint, fast execution)
- cross-platform (Linux, Windows, Mac OS X, FreeBSD, Solaris)
- dependent only on other Open Source software"
--Source: http://www.flamerobin.org/
It is easily installed on BackTrack (or other distros that utilize apt):
<
root@bt:~# apt-get install flamerobin
To run, launch X windows and type:
root@bt:~# flamerobin
You may get the following error message, ignore it and continue:
root@bt:~# The configuration file:
/root/.flamerobin/fr_databases.conf does not exist or cannot be opened.
This is normal for first time users. You may now register new servers and databases.
gsec (DB MGMT Tool)
This is the official tool to interact locally with the Firebird Database. gsec is a command line utility used to connect to the security.fdb in order to manage users. This tool must be run on the database server itself as it has no parameter to be run remotely, however this could be combined with psexec for remote execution if you had sufficient OS credentials.Interrogating the Database
With access to the database, you can do any number of tasks. We'll look a couple to get you started.Retrieve Remote Server Version
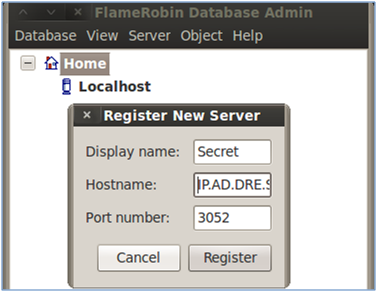
Using FlameRobin, first “register” the remote server so you are able to communicate with it. First open the FlameRobin GUI, then goto Server -> Register Server -> and enter the following:- Display name: Friendly name to call the host, I use the IP
- Hostname: Hostname or IP address
- Port Number: will usually be 3050, however this instance is running on another port.
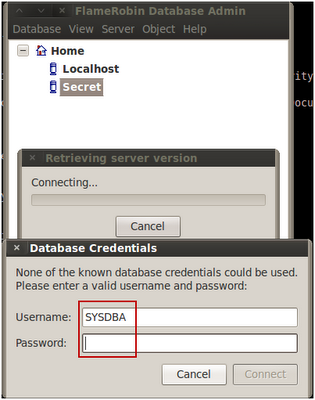
Next, right click on the server that you just registered, choose "Retrieve server version" and provide your credentials. The default firebird username and password is usually:
Username: SYSDBA
Password: masterkey
You should be provided the version number as shown below:
Adding/Changing Users
Another useful task is to add or change user accounts. An interesting piece of information is that the Firebird database does not check any characters beyond 8 in a password. Thus the masterkey default password might as well be “masterke” as the ‘y’ at the end is never checked because it is beyond 8 characters. Additionally, usernames are not case sensitive, however passwords are CaSe SeNsItIvE.With FlameRobin
Use the instructions above in the “Retrieve Remote Server Version” section in order to register the remote server if you have not done so already. Then right-click on the server that you just registered, select "Manage Users" and enter the SYSDBA credentials if they are not saved from the remote version enumeration above.To add a user, just click "Add User" and provide the required information! To modify other users (including changing their passwords) by clicking on the “details” icon which looks like a magnifying glass over a piece of paper.
With gsec
Since gsec a command line utility used to connect to the security.fdb in order to manage users, it must be run on the database server itself as it has no parameter to be run remotely. However, this could be combined with psexec for remote execution if you have sufficient OS credentials.Common command line options:
-di[splay]
Display all rows from security.fdb
-di[splay] name
Display information only for user name
-a[dd] name -pw password
Add a user named user with a password of password.
-mo[dify] name [options]
Modify the account name, optionally as specified by options.
-de[lete] name
Delete user name from security.fdb
-h[elp] or ?
Displays gsec commands and syntax
To add a "
Tony" user with the password of "S3kR3tP4$$": gsec -user sysdba -pass masterkey -add Tony -pw S3kR3tP4$$
To modify users, define the username and password used to connect to the database with "
-user" and "-pass", then use the "-mo" parameter to define the user account and "-pw" to define the new password. gsec -user sysdba -pass masterkey -mo -pw
Mitigation
The easiest way to help protect yourself is to change the default password to something complicated! Go to a command shell, cd to the Firebird bin subdirectory and issue the following command to change the password: gsec -user sysdba -pass masterkey -mo sysdba -pw
Notice that you specify “sysdba” twice in the command:
With the
-user parameter you identify yourself as SYSDBA. You also provide SYSDBA's current password in the -pass parameter. The -mo[dify] parameter tells gsec that you want to modify an account – which happens to be SYSDBA again. Lastly, -pw specifies the type of modification: the password. --Source: http://www.firebirdsql.org/manual/qsg2-config.htmlMore Info
- http://www.firebirdsql.org/manual/qsg2-config.html
- http://www.ibphoenix.com/download/tools/admin
- http://www.crypton.co.uk/freetools.html